Thermodynamics System: In thermodynamics the system is defined as the quantity of matter or region in space upon which the attention is concentrated for the sake of analysis. These systems are also referred to as thermodynamics system.
Boundary: It is bounded by an arbitrary surface called boundary. The boundary may be real or imaginary, may be at rest or in motion and may change its size or shape.

Surrounding: Everything out side the arbitrary selected boundaries of the system is called surrounding or environment.
The union of the system and surrounding is termed as universe.
Universe = System + Surrounding
Types of system
The analysis of thermodynamic processes includes the study of the transfer of mass and energy across the boundaries of the system. On the basis the system may be classified mainly into three parts.
- Open system.
- Closed System.
- Isolated system

Open system
The system which can exchange both the mass and energy (Heat and work) with its surrounding. The mass within the system may not be constant. The nature of the processes occurring in such system is flow type.
For example
1. Water Pump: Water enters at low level and pumped to a higher level, pump being driven by an electric motor. The mass (water) and energy (electricity) cross the boundary of the system (pump and motor).
2.Scooter engine: Air arid petrol enter and burnt gases leave the engine. The engine delivers mechanical energy to the wheels.
3. Boilers, turbines, heat exchangers. Fluid flow through them and heat or work is taken out or supplied to them. Most of the engineering machines and equipment are open systems.
Closed System
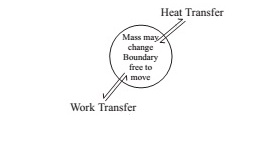
The system, which can exchange energy with their surrounding but not the mass. The quantity of matter thus remains fixed. And the system is described as control mass system. The physical nature and chemical composition of the mass of the system may change. Water may evaporate into steam or steam may condense into water. A chemical reaction may occur between two or more components of the closed system.
For example
1. Car battery, Electric supply takes place from and to the battery but there is no material transfer.
2. Tea kettle, Heat is supplied to the kettle but mass of water remains constant.
 3. Water in a tank
3. Water in a tank
4. Piston – cylinder assembly.
Isolated System
In an Isolated system, neither energy nor masses are allowed to cross the boundary. The system has fixed mass and energy. No such system physically exists. Universe is the only example, which is perfectly isolated system.


